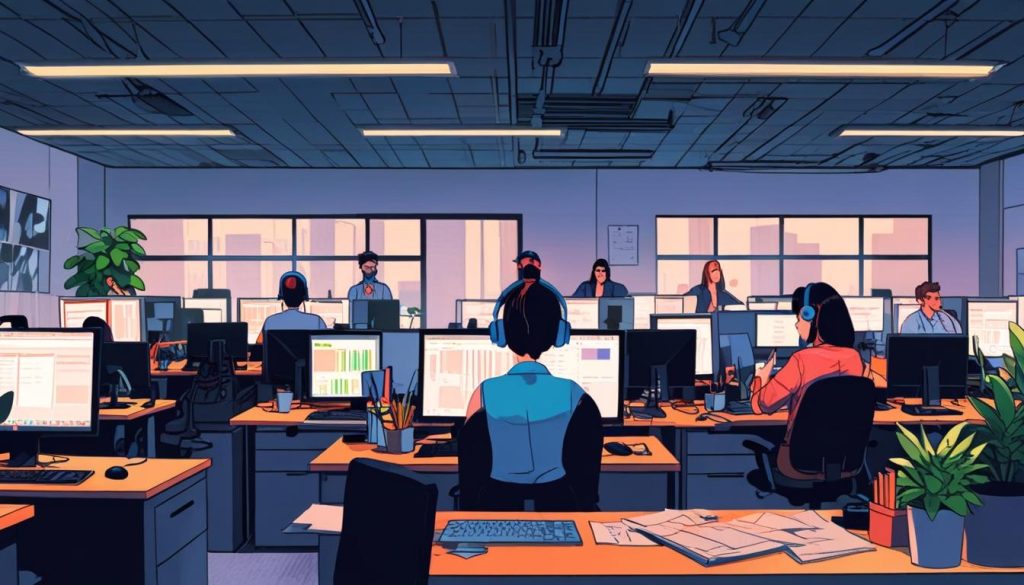
Recent research from Ohio State University has shed light on the potentially detrimental effects of background music in workplaces. With over 13.5 million people in the United States employed in environments where background music is prevalent, it is crucial to understand how musical choices impact employee well-being and productivity. The study highlights how music, often selected to please customers rather than incorporate employees’ needs, can inadvertently lead to negative consequences such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and heightened workplace dissatisfaction.
The research comprised two distinct studies. The first included 166 full-time employees who assessed four musical characteristics: volume, tempo, complexity, and emotional intensity. Participants were then asked to complete a creativity task while listening to one of two playlists. The first featured upbeat pop songs with moderate complexity, while the second offered a slower, gloomier selection played at a lower volume. The findings were telling; when the music did not align with the listening needs of the participants, they experienced significant adverse effects. This misalignment was especially impactful for individuals struggling with sensory filtering—the ability to focus on a specific sensory input—which often made it challenging for them to concentrate amid distracting sounds.
The second study involved 68 employees whose daily routines routinely included background music. Over a three-week period, these participants provided feedback on their musical preferences, mood, cognitive fatigue, and workplace behaviour through daily email surveys. The results reinforced the first study’s conclusions, showing that music not only modified participants’ emotional states but also could lead to counterproductive behaviours, such as slower work, negative remarks about the workplace, and even minor theft. When the music did not resonate with their tastes, employees exhibited reduced motivation to engage positively with colleagues or contribute extra effort.
Kathleen Keeler, co-author of the study and an assistant professor at Ohio State University, expressed that finding a balance in music selection is essential for businesses. “Employers need to try to balance making their music appealing to both customers and employees because that is not a trivial matter. If employees are unhappy, it doesn’t do the business any good,” she noted. This sentiment aligns with broader discussions in workplace ergonomics, suggesting employers explore methods to create musical environments supportive of both employee and customer satisfaction.
Experts in the field advocate for measures that would allow employees to find respite from incessant music during breaks. This could include dedicated quiet spaces or investing in smart headphone technology, which enables employees to tune in to customer interactions while filtering out disruptive background noise.
While the study highlighted the impact of inadequately chosen background music, it also hinted at potential benefits if employees were allowed to listen to their preferred tunes. The idea is supported by existing literature indicating that music can play a significant role in boosting productivity through reductions in stress and enhancing focus. Notably, background music has been shown to mask distracting sounds, thereby fostering an environment conducive to concentration, especially during tasks requiring significant cognitive effort.
Research has long debated the influence of music on productivity. For instance, older studies have reported mixed findings; while some indicated that employees enjoyed music in the workplace, they often found no significant increase in productivity levels. Conversely, subsequent research, including a study by neuropsychologists at Mindlab International, revealed that around 81% of workers completed tasks more swiftly while listening to music, with pop music in particular leading to noteworthy improvements in efficiency.
Moreover, the benefits of background music extend beyond individual tasks. Studies indicate that music can foster cooperation among employees, as those exposed to upbeat musical selections tend to engage more collaboratively amongst their colleagues. This suggests that the right musical environment can harmonise the workplace dynamics, promoting both morale and productivity.
As employers navigate the complexities of creating an inviting atmosphere, understanding the nuanced relationship between music, employee satisfaction, and productivity remains paramount. Ultimately, the choice of background music may be more than a simple ambient decision; it can significantly influence not only the well-being of individual employees but also the overall performance and success of the organisation.
Reference Map
- Paragraph 1: [1]
- Paragraph 2: [1]
- Paragraph 3: [1]
- Paragraph 4: [1]
- Paragraph 5: [1], [2], [3]
- Paragraph 6: [3], [4]
- Paragraph 7: [5], [6], [7]
Source: Noah Wire Services