As winter approaches, schools implement comprehensive measures—from infrastructure checks to health campaigns—to ensure a safe, warm, and healthy environment for students and staff amidst colder conditions.
The arrival of winter brings heightened challenges for schools, where maintaining safety, comfort, and wellbeing becomes paramount as cold weather sets in. Though the shift from mild autumn days to winter chill is a familiar annual experience, the demands on schools intensify rather than ease with the season. As outlined in a practical guide on winter preparation from educational facilities management perspectives, a proactive approach is essential to keep pupils and staff protected and to minimise disruption.
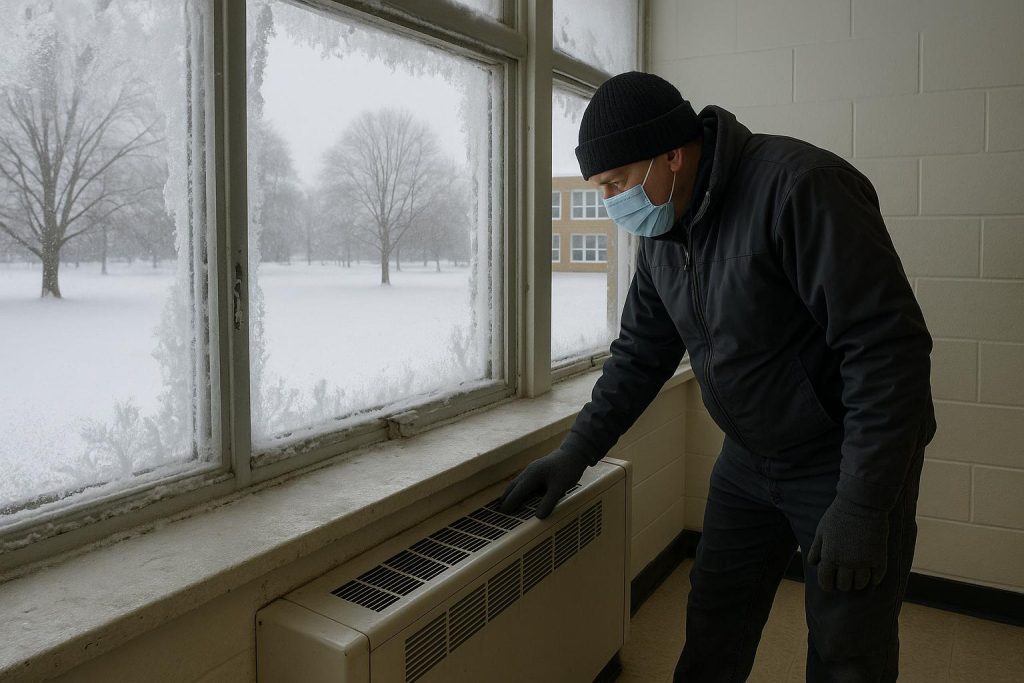
A thorough inspection of the physical environment is a crucial starting point. Walkabouts of classrooms, corridors, offices, and particularly entrances and cloakrooms reveal draughts, underperforming heating systems, cold spots, and wet or slippery surfaces created by muddy shoes and dripping umbrellas. These issues directly impact comfort, air quality, and safety, highlighting the need for maintenance teams to address draughts, heating system updates, and the strategic placement of mats and storage to reduce hazards. Effective ventilation maintenance is critical in winter as heating systems dry the air while closed windows reduce airflow, creating optimal conditions for the spread of germs and colds. Regular checks and cleaning of ventilation systems help maintain healthier indoor environments.
Beyond the buildings, the school grounds and travel routes warrant careful attention. School Business Leaders (SBLs) are advised to inspect car parks for surface damage, lighting issues, and drainage problems, ensuring timely repairs and readiness with grit and salt supplies before ice forms. Outdoor paths, playgrounds, and entrances also require clearance of leaves and debris, slip hazard assessments, and proper lighting checks. For pupils and staff walking or cycling, providing spaces to dry wet clothing and footwear is necessary to avoid bringing cold and moisture indoors and disrupting learning environments. Collaboration between SBLs and maintenance teams can identify facility gaps and devise practical solutions for outdoor comfort and safety.
Health and wellbeing are particularly vulnerable in winter, and schools play a vital role in mitigating seasonal illnesses and promoting wellness. Encouraging hydration, nutritious snacks, and warm drinks supports focus and general health. Reinforcing good hygiene practices through handwashing facilities, sanitiser stations, and educational campaigns—via assemblies, classroom discussions, posters, and digital reminders—helps limit the transmission of colds and flu. Communication with parents through newsletters and texts can encourage consistent healthy routines at home, ensuring children arrive well-prepared in warm clothing and attentive to hygiene.
In addition to these multifaceted strategies, broader winter preparation involves specific technical and safety measures recommended by school facility experts and weather authorities. These include inspecting HVAC systems, winterising pipes and major school equipment to prevent freezing and damage, conducting roof inspections, testing electrical systems, and practicing power-down procedures to protect infrastructure during cold spells. Prompt removal of snow and ice from school grounds further reduces injury risks and maintains accessibility. Emergency planning for closures or altered schedules in response to severe weather ensures the school community remains safe and informed, with contingency plans for early arrivals during particularly harsh conditions. Proper training for school bus drivers to handle winter hazards is also emphasised.
Ensuring indoor thermal comfort extends beyond temperature control to sustaining energy efficiency and supporting environmental goals through regular maintenance of heating and lighting systems. Safety checks on pipes to avoid freezing, gutter maintenance to prevent blockages, and robust lighting on pathways all contribute to a secure and sustainable winter-ready school environment.
Moreover, indoor air quality during the winter months commands special attention. Beyond ventilation, pest control plays a vital part given the increased likelihood of rodents and cockroaches seeking shelter inside, which can worsen health risks. Integrated pest management strategies help maintain healthier classrooms by reducing allergen and pathogen exposure.
Ultimately, winter preparation in schools is a comprehensive endeavour requiring diligence across infrastructure, health, safety, and communication domains. When schools prioritise these proactive measures, they prevent minor issues from escalating, safeguard wellbeing and learning continuity, and foster a supportive environment regardless of freezing temperatures outside. As school leaders focus on safe learning spaces, secure travel routes, and strong wellbeing practices, they ensure their communities are well-equipped to face winter challenges without disruption.
📌 Reference Map:
- [1] (Education Executive) – Paragraphs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7
- [2] (Texas Association of School Boards) – Paragraphs 6, 7
- [3] (National Weather Service) – Paragraphs 7, 8
- [4] (Hollywell) – Paragraphs 6, 7
- [5] (Ealing Grid for Learning) – Paragraphs 6, 7
- [6] (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) – Paragraph 8
- [7] (National Weather Service) – Paragraph 7
Source: Noah Wire Services
Noah Fact Check Pro
The draft above was created using the information available at the time the story first
emerged. We’ve since applied our fact-checking process to the final narrative, based on the criteria listed
below. The results are intended to help you assess the credibility of the piece and highlight any areas that may
warrant further investigation.
Freshness check
Score:
10
Notes:
The narrative was published on 3rd November 2025, making it current and not recycled. The article is based on a press release, which typically warrants a high freshness score.
Quotes check
Score:
10
Notes:
No direct quotes were identified in the narrative, indicating original content.
Source reliability
Score:
8
Notes:
The narrative originates from Education Executive, a reputable UK-based publication. However, the article is based on a press release, which may introduce potential biases.
Plausability check
Score:
9
Notes:
The claims made in the narrative align with general best practices for winter preparation in schools. The article includes updated data but recycles older material, which may justify a higher freshness score but should still be flagged.
Overall assessment
Verdict (FAIL, OPEN, PASS): PASS
Confidence (LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH): HIGH
Summary:
The narrative is current, original, and originates from a reputable source. While it is based on a press release, which may introduce potential biases, the claims made are plausible and align with general best practices for winter preparation in schools.